반응형
Bfs (너비 우선 탐색, Breadth-First Search), Dfs (Depth First Search)
BFS는 그래프 탐색 알고리즘이다. 루트 노드(혹은 다른 임의의 노드)에서 시작해서 인접한 노드를 먼저 탐색하는 방법이다 즉, 정점들과 같은 레벨에 있는 노드들을 먼저 탐색한다.
DFS는 깊이를 우선 탐색한다. 같은 레벨이 아니라 바로 아래 레벨에 있는 자식 노드의 끝까지 탐색하고 자식이 없다면 돌아오는 방식이다.
진행 순서 예시
아래와 같은 그래프가 있는 경우 BFS와 DFS의 탐색 순서를 알아보면 다음과 같다.
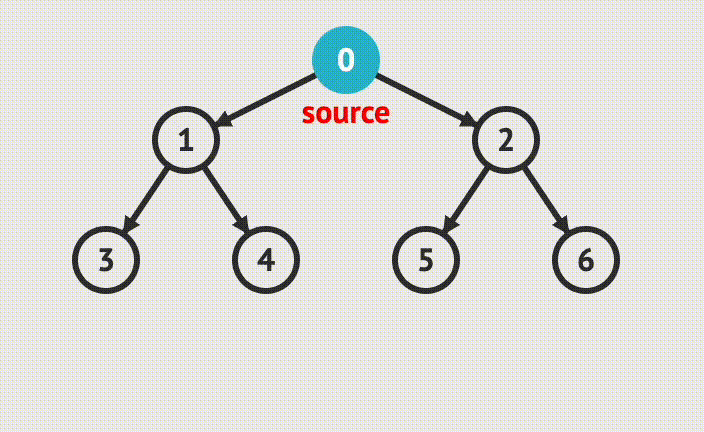
- BFS
- 다음 레벨로 하나씩 넘어가면서 같은 레벨에 있는 노드들을 먼저 방문한다.
- 실행순서 : 0 -> 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> 6
- DFS
- 한 노드의 자식을 끝까지 방문하고, 다시 타고 올라와서 다른 노드의 자식을 타고 동일하게 끝까지 방문한다.
- 실행순서 : 0 -> 1 -> 3 -> 4 -> 2 -> 5 -> 6
자바로 구현
BFS는 Queue, DFS는 Stack으로 구현한다.
코드는 거의 유사하지만, 다른점은 DFS는 시작 노드를 방문한 노드를 표시하는 Visited에 추가하지 않는다.
추가하지 않는 이유는 중복된 노드를 처리하지 않기 때문인데, BFS는 큐에 넣을 때 방문 처리를 하게되고, DFS는 stack에서 꺼낼 때 방문 여부를 확인하는 구조적인 차이가 있기 때문이다.
(Queue: FIFO, Stack: LIFO)
public class BfsDfsSearch {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<Integer, List<Integer>> graph = new HashMap<>();
graph.put(0, Arrays.asList(1, 2));
graph.put(1, Arrays.asList(3, 4));
graph.put(2, Arrays.asList(5, 6));
graph.put(3, new ArrayList<>());
graph.put(4, new ArrayList<>());
graph.put(5, new ArrayList<>());
graph.put(6, new ArrayList<>());
System.out.println("BFS 탐색 결과:");
bfs(graph, 0);
System.out.println("DFS 탐색 결과:");
dfs(graph, 0);
}
// BFS 구현
public static void bfs(Map<Integer, List<Integer>> graph, int startNode) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
Set<Integer> visited = new HashSet<>();
queue.add(startNode);
visited.add(startNode);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int currentNode = queue.poll();
System.out.print(currentNode + " ");
// 인접 노드
for (int neighbor : graph.get(currentNode)) {
if (!visited.contains(neighbor)) {
queue.add(neighbor);
visited.add(neighbor);
}
}
}
}
// DFS 구현
public static void dfs(Map<Integer, List<Integer>> graph, int startNode) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
Set<Integer> visited = new HashSet<>();
stack.push(startNode);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
int currentNode = stack.pop();
if (!visited.contains(currentNode)) {
visited.add(currentNode);
System.out.print(currentNode + " ");
// 인접 노드를 역순으로 스택에 추가
List<Integer> neighbors = graph.get(currentNode);
Collections.reverse(neighbors);
for (int neighbor : neighbors) {
if (!visited.contains(neighbor)) {
stack.push(neighbor);
}
}
}
}
}
}BFS, DFS 시간 복잡도
- BFS와 DFS의 시간 복잡도는 그래프의 노드 수(V)와 간선 수(E)에 따라 결정된다.
- 구현된 코드에서
while반복문은:- 모든 노드(Vertex)를 방문하고,
- 각 노드에서 연결된 간선(Edge)을 따라가며 탐색한다.
- 그래프를 인접 리스트(Adjacency List)로 표현했으므로,
- 노드를 방문하는 작업은
O(V), - 간선을 탐색하는 작업은
O(E)가 된다.
- 노드를 방문하는 작업은
- 따라서 총 시간 복잡도는 O(V + E)이다.
반응형